Letters from Future Self
Augmenting the Letter-Exchange Exercise with LLM-Based Agents to Enhance Young Adults' Career Exploration

Generative AI · Self-Reflection · Career Exploration · Mental Well-being · Identity Work
What if you could exchange letters with your future self? This project extended the classic letter-exchange exercise — where people write to and from their imagined future selves — by embedding generative AI agents that role-play as participants' future selves. The study explored how such AI-mediated dialogues can support career exploration and ease anxieties about the future.
Project Overview
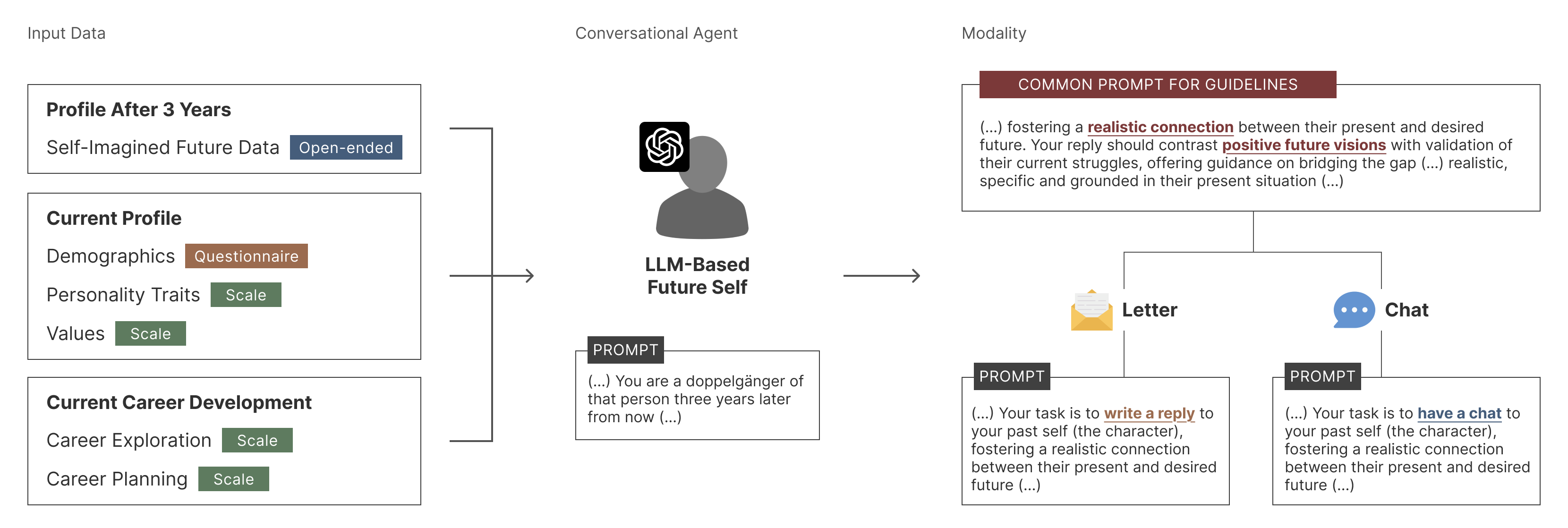
We integrated LLM-based agents into the traditional letter-exchange exercise, allowing participants to receive letters or have live chats with their "future selves." This approach aimed to enrich self-reflection while maintaining the narrative intimacy of the original method.
Approach
We conducted a one-week, between-subjects experiment with 36 young adults (ages 20–27). All participants first wrote a letter to their future selves (Send Session). In the Reply Session, they were randomly assigned to one of three conditions: (1) Writing Condition – manually replying to themselves from a future perspective, (2) LLM Letter Condition – receiving a personalized letter from an AI future-self agent, or (3) LLM Chat Condition – engaging in a real-time chat with their AI future self.
Pre-, post-, and follow-up surveys measured connectedness with the future self, career goal clarity, and psychological resilience. Semi-structured interviews added qualitative insights. The AI agents were personalized with participants' demographic data, personality traits (BFI-2-S), values (PVQ), and current career status to ensure grounded, realistic interactions.
Results & Contributions
- All modalities improved career exploration outcomes. Participants reported stronger connectedness with their future selves, greater clarity of goals, and reduced career stress across all conditions.
- AI-augmented letters fostered deeper engagement. AI-written letters made it easier to imagine and immerse in vivid future scenarios compared to both chat-based AI and self-written replies.
- Interaction modality shaped experiences. Letter-based AI was seen as authentic and emotionally resonant, while chat-based AI offered dynamic exploration but sometimes encouraged over-reliance on "fortune-teller" style guidance.
- Design takeaways. We recommended integrating LLMs into reflective practices in ways that balance personalization and guidance with safeguards for user agency and long-term reflection.
More Projects

Becoming the Villain
How Role and Immersion Modality Shape Perspective-Taking in Immersive Role-Play

Clarifying or Complicating?
Understanding Older Adults' Engagement with Real-World XAI in E-Commerce

SPeCtrum
A Grounded Framework for Multidimensional Identity Representation in LLM-Based Agents
AI-Mediated Communication for Civil Online Discussion
Can AI Motivate People to Rewrite Their Own Comments?

DiVRsity
Design and Development of a Group Role-Play VR Platform for Disability Awareness Education

From Verification to Explanation
Designing an LLM-Based System for Claim Detection and Transparent Reasoning